Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6 Solutions for class 6 CBSE, Stepwise Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6, Class 6th Maths solutions wikipedia, Questions and Answers for NCERT Mathematics Class 6, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Mathematics Class Sixth Exercise 4.6 of Chapter 4, CBSE Class sixth Maths Solutions, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6, Detailed Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6, Stepwise Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Exercise 4.6, Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 4, Stepwise and detailed solutions for NCERT Class 6 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.6, Detailed Solutions for Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics, NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6, Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6 NCERT Solutions.
Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 4 – Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6
1. From the figure, identify :
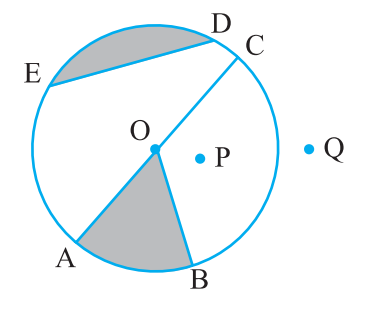
(a) the centre of circle
Ans: O is the centre of the circle
(b) three radii
Ans: OC, OA , OB are radii of the circle
(c) a diameter
Ans: AC is the diameter of the circle
(d) a chord
Ans: ED is a chord of the circle
(e) two points in the interior
Ans: Points O and P are in the interior of the circle
(f) a point in the exterior
Ans Point Q is in thee exterior of the circle
(g) a sector
Ans: AOB is the sector of the circle
(h) a segment
Ans: ED is the segment of the circle
2. (a) Is every diameter of a circle also a chord?
Ans: Yes, every diameter is also a chord.
Because chord connects two points of a circle and diameter is a chord which passes through centre of a circle..
(b) Is every chord of a circle also a diameter?
Ans: No, every chord of a circle is not the diameter.
Because for a chord to be the diameter it should passes through the centre of the circle.
3. Draw any circle and mark
Ans:
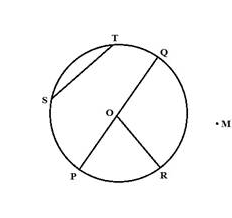
(a) its centre
Ans: O is the centre of the circle
(b) a radius
Ans: OP, OR, OQ are the radii of the circle
(c) a diameter
Ans: PQ is the diameter of the circle
(d) a sector
Ans: POR is a sector of the circle
(e) a segment
Ans: ST is a segment of the circle
(f) a point in its interior
Ans: O is in the interior of the circle
(g) a point in its exterior
Ans: M is in the exterior of the circle
(h) an arc
Ans: PR is an arc of the circle
4. Say true or false :
(a) Two diameters of a circle will necessarily intersect.
Ans: True, because both will pass through the centre
(b) The centre of a circle is always in its interior
Ans: True
You can find the solutions for Class 6 Mathematics previous exercises from here
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.5 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.4 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.3 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.2 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.1 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.7 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.6 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.5 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.4 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.3 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.2 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.1 Solutions
- Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.3 Solutions
- Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.2 Solutions
- Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.1 Solutions
- Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.3 Solutions
- Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.2 Solutions
- Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.1 Solutions

