Perpendicular lines, Adjacent lines, perpendicular bisectors, Perpendicular, Not perpendicular, Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5 Solutions for class 6 CBSE, Stepwise Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5, Class 6th Maths solutions Wikipedia, Questions and Answers for NCERT Mathematics Class 6, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Mathematics Class Sixth Exercise 5.5 of Chapter 5, CBSE Class sixth Maths Solutions, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5, Detailed Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5, Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5, Stepwise Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Exercise 5.5, Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 5, Stepwise and detailed solutions for NCERT Class 6 Chapter 5 Exercise 5.5, Detailed Solutions for Solutions for NCERT Class 6 Mathematics, NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5, Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5 NCERT Solutions.
Questions and Solutions for NCERT Class 6th Mathematics Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.5
1. Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines :
(a) The adjacent edges of a table top.
Ans: Perpendicular
(b) The lines of a railway track.
Ans: Not perpendicular
(c) The line segments forming the letter ‘L’.
Ans: Perpendicular
(d) The letter V.
Ans: Not Perpendicular
2. Let PQ be the perpendicular to the line segment XY . Let PQ and XY intersect in the point A. What is the measure of ∠PAY ?
Ans: ∠PAY = 90°
3. There are two set-squares in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
Ans: One set square has angles 90°, 45°, 45° and the other set-square has angles 30°, 60°, 90°. They have 90° angle as common angle.
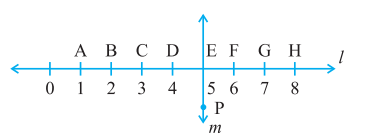
4. Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m
(a) Is CE = EG?
Sol: Measure of CE = 5 – 3 = 2 units
Measure of EG = 7 – 5 = 2 units
Therefore, CE = EG
(b) Does PE bisect CG?
Sol: Measure of EG = 7 – 5 = 2 units
Measure of CE = 5 – 3 = 2 units
EG = CE and CE + EG = CG
Therefore, PE bisects CG
(c) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
Ans: CG, DF and BH
(d) Are these true?
(i) AC > FG
Ans: True
AC = 2 units
FG = 1 units
So, AC > FG
(ii) CD = GH
Ans: True
CD = 1 unit
GH = 1 unit
So, CD = GH
(iii) BC < EH
Ans: True
BC = 1 unit
EH = 3 units
So, BC < EH
You can find the solutions for Class 6 Mathematics previous exercises from here
- Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.4
- Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.3
- Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.2
- Understanding Elementary Shapes – Exercise 5.1
- Chapter Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.6 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.5 Solutions
- Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.4 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.3 Solutions
- Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.2 Solutions
- Basic Geometrical Ideas – Exercise 4.1 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.7 Solutions
- Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.6 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.5 Solutions
- Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.4 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.3 Solutions
- Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.2 Solutions
- Playing with Numbers – Exercise 3.1 Solutions
- Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.3 Solutions
- Chapter 2 Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.2 Solutions
- Whole Numbers – Exercise 2.1 Solutions
- Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.3 Solutions
- Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.2 Solutions
- Knowing Our Numbers Solutions Exercise 1.1 Solutions