Combustion And Flame
Combustion
Burning of any substance is defined as combustion.
Combustion is defined as the process of burning something.
Example: Burning of coal, paper, candle, etc.
In chemical change, the change that takes place cannot be reversed.
For example: Burning paper converts it into ash and ash cannot be changed back into paper. Physical change is a temporary change and can be reversed and no new substance is formed. For example: If ice melts it can be reconverted into ice without forming any new substance.
Burning of coal also gives energy in the form of light and heat. In this process, the composition of new substance gets changed.
On burning of paper, the composition of ash always gets changed. Oxygen gas is usually used as a supporter of combustion.
Charcoal burns in air to give carbon dioxide and heat.
C + O2 → CO2 + Heat
Methane burns in air and forms carbon dioxide, water and heat.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
Conditions required for combustion
The following conditions are necessary for combustion-
- Combustible substance
- Supporter of Combustion that is Oxygen Gas
- Ignition Temperature
Substances can be divided into two parts:
1)Combustible substances 2)Non Combustible Substances
Combustible substances
Substances that easily catch fire are called combustible substances. For example: Kerosene, Petrol etc.
Non combustible substances
Substances which do not burn in air or oxygen . Substances that do not catch fire easily are called non combustible substances. For example: Glass, Stone etc.
Ignition Temperature
It is the lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire. It is different for different substances.
For example: kerosene oil does not burn unless it is heated up to its ignition temperature.
Matchsticks
Since ages, matchsticks are in use for burning substances . Modern matchsticks are made up with mixture of antimony trisulphide and potassium chlorate with some glue and starch applied on the head of the match. The rubbing surface has powdered glass and some red phosphorous. On striking match against rough surface, red phosphorous gets converted into white phosphorous and it reacts with potassium chlorate to ignite antimony trisulphate and so, combustion takes place.
Types of Combustion
There are three types of combustion which are as follows-
- Spontaneous
- Rapid
- Explosive
Spontaneous combustion
It is combustion that occurs at room temperature on its own. It is shown by substances that have an ignition temperature less than room temperature.
For example: Burning of yellow phosphorous. In summers, Yellow phosphorous catches fire itself even at room temperature.
Many disastrous fires in coal mines result due to this kind of combustion. The heat rays coming from the sun or a lightning strike might be responsible for this kind of combustion.
Rapid Combustion
It occurs rapidly, evolving a lot of heat and light in a short period of time. For example: LPG( Liquified Petroleum Gas), Kerosene oil, Coal etc.
Example: Bring a burning matchstick or a gas lighter near a gas stove in the kitchen. Turn on the knob of the gas stove. We find that the gas burns rapidly and produces heat and light.
Coal catches fire rapidly and gives a lot of heat and light. This energy is used for different processes.
Explosive Combustion
It is the combustion that occurs extremely fast with release of heat and light and also loud sound. For example: Crackers.
When a fire cracker is ignited, a sudden reaction takes place with the evolution of heat, light and sound with the large amount of gas.
Fire Extinguisher
- Foam type fire extinguisher
- Soda acid type extinguisher
Flame
A flame is a hot bright stream of burning gas that comes from something that is burning.
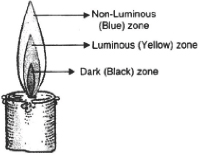
It consists of three zones
- Dark inner zone 2.Middle zone 3.Outermost zone
Dark inner zone
- It is black in color.
- It is innermost close to wick.
- It consist of unburnt vapours of wax.
- It is known as no combustion zone.
Therefore, it is least hot.
Middle zone
- It is luminous zone.
- Zone of incomplete combustion. In this zone, partial combustion takes place.
- It is yellow in color.
Therefore, it is somewhat hot.
Outermost zone
- It is the hottest zone.
- It is the result of complete combustion.
- It is the non-luminous zone.
- It is blue in color and faintly visible.
Fuel
The substance that undergoes combustion is called fuel. For example: Petrol, Diesel, Coal, wood, charcoal etc.
Types of Fuels
Solid fuels: It includes Coke, Coal, Wood etc.
Liquid fuels: It includes Petrol, Diesel, Kerosene.
Gaseous fuels: It includes LPG, CNG etc.
All of these fuels produce energy on burning.
Characteristics of good Fuel
- It should be easy to store and transport.
- It should burn smoothly without emitting harmful gases.
- It should not produce smoke.
- It should be easy to store and transport.
- It should have moderate ignition temperature.
- It should have high calorific value.
Ideal Fuel
The fuel which satisfies all the characteristics of good fuel is termed as an ideal fuel.
Probably, there is as such no ideal fuel present. But liquid and gaseous fuels are better.
Calorific value
It is amount of heat released when 1 gram of fuel is completely burned in sufficient supply of oxygen.It is measured in kilojoules per gram.
For example: Hydrogen gas.
Burning of Fuels
Global warming
Combustion of most fuels leads to an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that has lead to increase in the average temperature on the earth. It leads to ecological imbalance including melting of polar glaciers and causing floods.
Acid rain
Burning of coal and diesel produces sulphur dioxide gas which can cause suffocation and also it can lead to acid rain.
Prevention from Acid rain
The use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles is being replaced by CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), because CNG produces harmful products in very small amounts. CNG is a cleaner fuel
EXERCISES
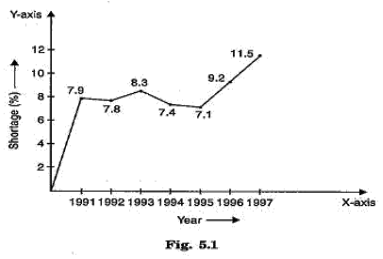
1.The conditions under which combustion can take place are presence of oxygen,presence of inflammable substance and ignition temperature.
2. a) pollution (b) kerosene (c) ignition temperature (d) water.
- Combustion of fuels like petroleum causes formation of un-burnt carbon particles along with carbon monoxide gas. These harmful pollutants enter the air and cause respiratory diseases. It is a comparatively cleaner fuel. Therefore, the use of CNG has reduced pollution in our cities..
4.Comparison

5.(a) Water is a good conductor of electricity. It conducts electricity and may result electric shock.
(b) LPG has more calorific value and produces no pollution. So it is better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) The ignition temperature of paper is less, so it catches fire easily. It does not catch fire when wrapped around aluminium pipe because aluminium absorbs the heat, so paper does not attain its ignition temperature.
6.
- Kilojoules per kg (kJ/kg)
- (i) CO2forms a blanket around fire due to which supply of air is stopped.
(ii) CO2 also brings down the temperature of the fuel.
- The green leaves contain some water due to which the ignition temperature of leaves increases and they do not catch fire easily while dry leaves have no water, so they catch fire easily.
- A goldsmith uses the outer zone (non-luminous zone) of a candle flame to melt gold and silver because it is the hottest zone and has more temperature.
- Total mass of fuel = 4.5 kg
Total heat produced = 180,000 kJ
Heat produced by burning 1 kg of fuel = 180,000 kJ/4.5 kg = 40,000 kJ/kg.
So, calorific value of fuel = 40,000 kJ/kg.
- Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts in which substance reacts with oxygen and gives out energy during the process in the form of heat or light or both. Rusting is kind of slow combustion as it is exothermic process as heat is released during rusting.
- The water heated by Ramesh will get heated in a shorter time because he kept his beaker near the hottest zone of the flame.